Comparative analysis of data stations in federated health data systems
This section provides a detailed comparative analysis using the concepts of the PHT architecture of how the “data station” concept is realized in existing federated data systems.
EUCAIM
PLUGIN
The PLUGIN federated learning network is an ongoing initiative initated in 2022 by DHD, IKNL and Expertisecentrum Zorgalgoritmen (EZA) [1]. Its main objective is to realize a federated learning network that includes all 70 hospitals in the Netherlands. The PLUGIN network is intended to support a wide variety of use-cases including:
- AI-assisted coding (ICD10) based on supervised learning with language models
- Automated data submission for national registries such as the Dutch Cancer Registry managed by IKNL
- Descriptive analytics, for example, performance analysis across hospitals for benchmarking purpose
The architecture of
Fair Data Cube
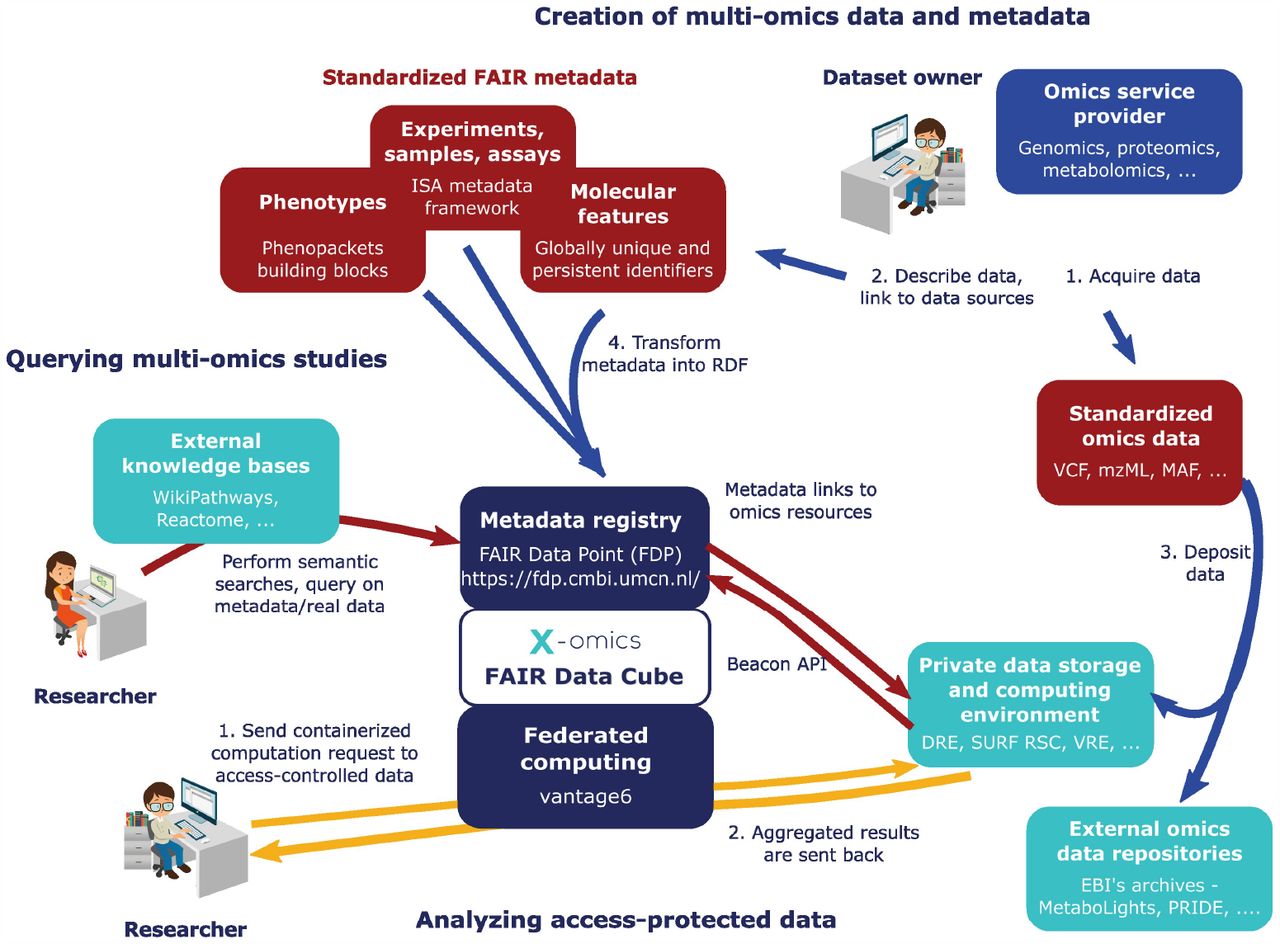
The Fair Data Cube [2] is a framework for the storage, analysis and integration of multi-omics data. Fair Data Cube reuses and extends existing open software components/modules and initiatives. This includes the FAIR Data Point [3] and vantage6 [4]. Further elements of the FDCube are the Investigation-Study-Assay (ISA) metadata framework[5, 6] for capturing general study metadata, sample (including basic sample characteristics), and assay metadata, and the Phenopackets [7] standards for capturing phenotypic description of a patient/sample. The concept of the FDCube is illustrated Figure 1.
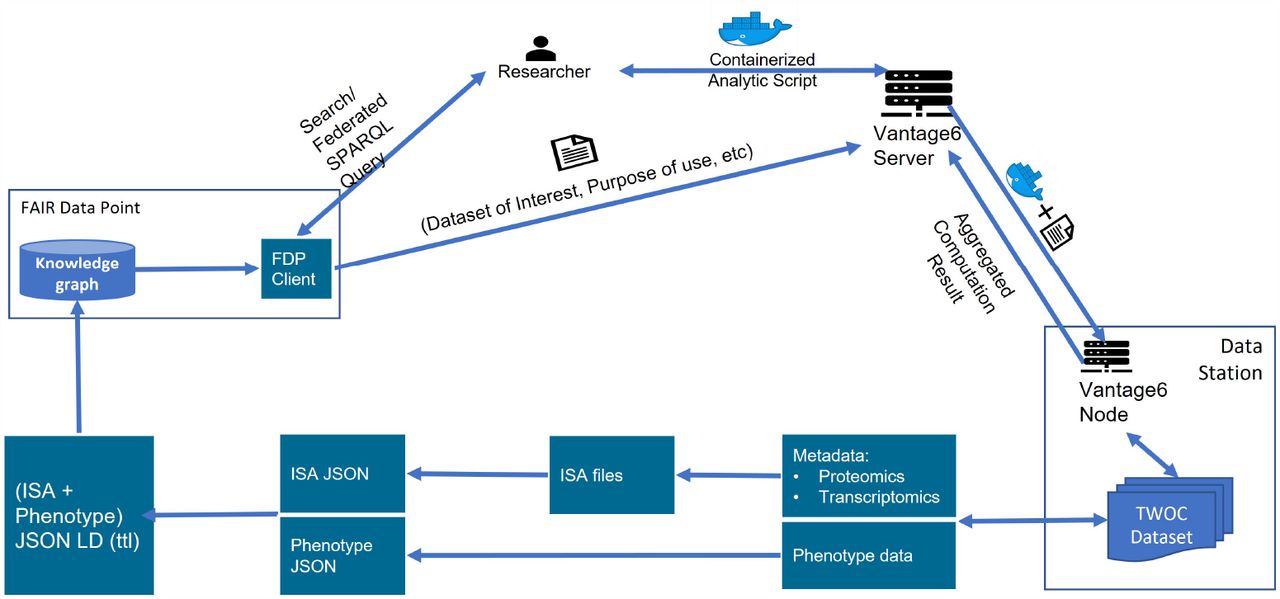
Figure 1 (a) shows an example of how Fair Data Cube is used on a public dataset on COVID-19 featuring multi-omics patient data. This dataset was prepared, harmonized and FAIRified as part of the TWOC project. The dataset consists of paired omics data layers describing transcriptomics, proteomics and metabolomics of blood samples, and includes comprehensive phenotype information. Both the ISA metadata schema and Phenopackets schema are adopted. The ISA metadata schema is used as a standard metadata schema to capture metadata about (-omics) experiments, and serializes in an ISA-json file using ISA tools. The ISA tools also provided additional functionalities to convert the ISA objects into linked data, for example a ttl (Terse RDF Triple Language) file. The FAIRified metadata of the TWOC dataset was published on a Fair Data Point portal allowing for querying using SPARQL. After finding an interesting dataset via browsing or by SPARQL, the researcher could further run follow-up analyses on the target dataset by raising a computation request to the Vantage6 server and retrieve the returning results from the data station via Vantage6.
Swiss Personal Health Network
The Swiss SPHN network [8] as an example of a data station that uses graph databases both for the data and metadata
Datastation-as-a-Service in KIK-V
The Datastation-as-a-Service as defined by the Zorginstituut for federated analytics using privacy-enhancing technologies [9]
Cumuluz data station
[TO DO]